New York, NY, December 11th, 2025, FinanceWire
New York, NY, December 11th, 2025, NewsDirect
New data from Marktechpost uncovers how machine learning is transforming scientific discovery worldwide — and which countries and institutions are driving the shift.
A first-of-its-kind analysis of more than 5,000 scientific articles published across the Nature family of journals between January 1 and September 30, 2025, reveals how deeply machine learning (ML) now influences global science.
The ML Global Impact Report 2025, covering research from more than 125 countries, identifies the most widely used ML tools in academic research and highlights the nations and institutions shaping the future of ML-enabled scientific discovery.
The findings show that ML is most broadly applied in the sciences and health research — especially in tasks such as prediction, classification, segmentation, and modeling. These include fields like early-detection imaging and precision diagnostics, genomic sequence mapping and mutation tracking, advanced robotics and materials engineering, and large-scale Earth-observation analytics.
Asif Razzaq, Editor & Co-Founder, Marktechpost:
“This report shows that machine learning isn’t just reshaping AI — it’s reshaping science itself. Across imaging, genomics, climate research, and robotics, ML has become a core part of how discoveries are made. The real story here is not hype, but impact: ML is now a fundamental instrument of modern scientific work.”
Matthew J. Hashim, Associate Director, Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, University of Arizona:
“Scientific research has moved beyond experimenting with machine learning to advancing entire fields through machine learning. The data make it clear: global science is now built on shared tools, shared methods, and shared collaborations. ML has become one of the most unifying forces in contemporary research.”
ML in Science: The Global Landscape
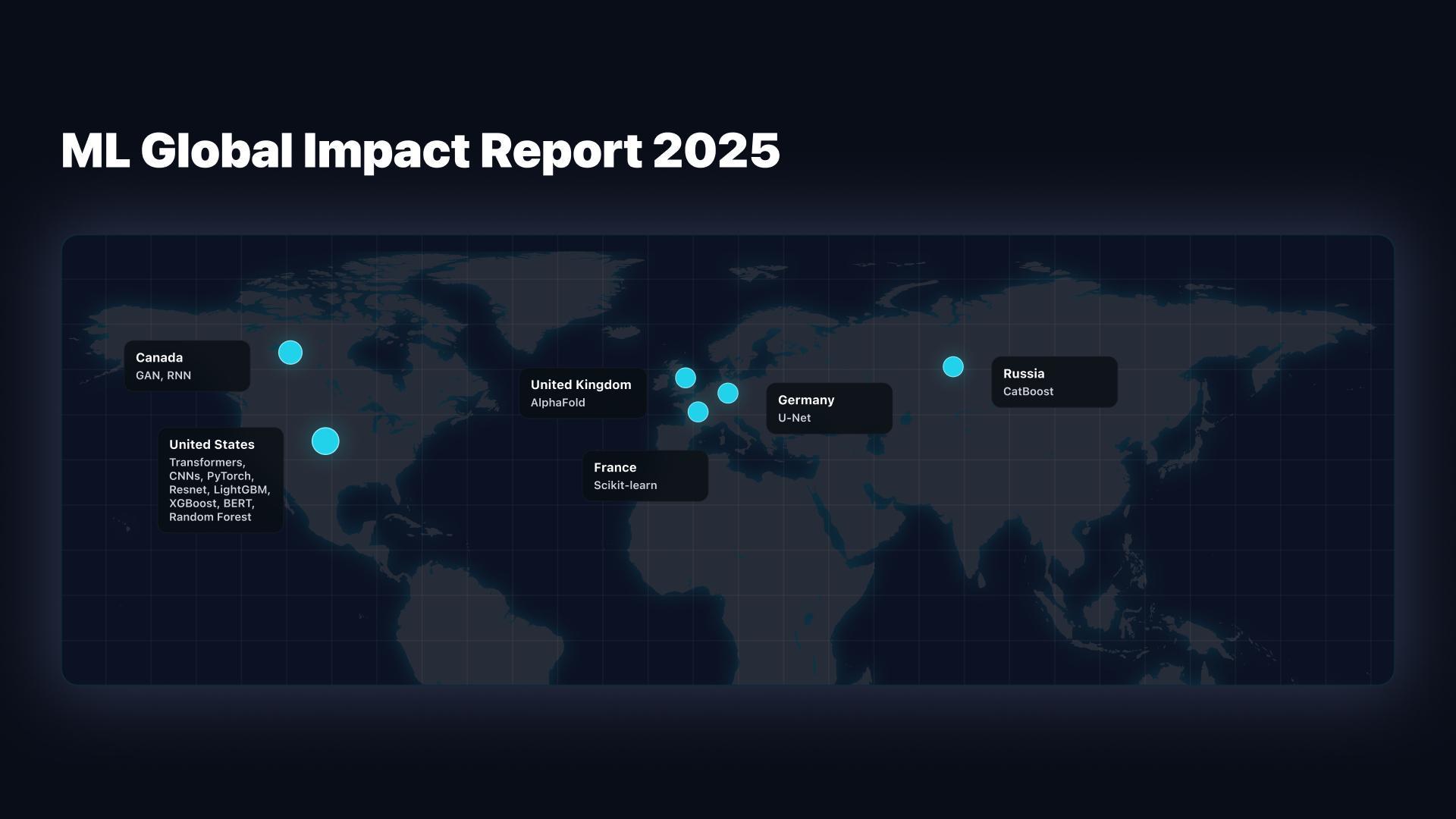
As ML becomes a standard part of scientific workflows around the world, the United States distinguishes itself through the breadth of ML techniques adopted across disciplines. According to the report, nearly 90% of the open-source ML tools referenced in 2025 scientific research originate from the U.S., including many of the world’s foundational frameworks used across domains such as imaging, genomics, and environmental science.
At the same time, China is the clear leader in publication volume, accounting for 43% of all ML-enabled papers globally — more than 2,100 studies in 2025. China’s scientific output reflects a high-density, high-throughput research model, with large numbers of ML-based studies emerging from a relatively focused group of major institutions.
The U.S., ranking second in total publication count at 18%, displays a far more distributed ecosystem. Universities, hospitals, national laboratories, and private research centers all contribute meaningfully, with Harvard Medical School leading the count of ML-enabled research among U.S. institutions.
While the U.S. dominates the origin of open-source ML tools, Europe contributes several of the most frequently referenced scientific ML models, including Scikit-learn (France), U-Net (Germany), and CatBoost (Russia). Other key non-U.S. contributions include GAN and RNN architectures from Canada.
Research Volume vs. Density
The report highlights meaningful differences in how national research ecosystems scale.
- China generates a high volume of ML-enabled science from a more concentrated pool of institutions, producing an average of 72.8 articles per university (normalized).
- The United States shows a larger, more diverse contributing base, averaging 39.6 articles per institution — reflecting its broad interdisciplinary adoption of ML.
- India and Saudi Arabia are emerging as fast-growing institutional players, with expanding ML-enabled research footprints and increasing participation in collaborative scientific networks.
These trends suggest that while China leads in output, other nations — including India, Saudi Arabia, and U.S. institutions — are shaping new hubs of ML-driven innovation beyond traditional centers of scientific leadership.
Collaboration: The Backbone of ML-Enabled Science
Across all regions, collaboration remains the default model for ML-driven scientific research. Most ML-enabled papers include 2–15 institutional affiliations, often combining a computational laboratory, a domain-specialist research institute, and a medical or industrial partner.
Only a small group of global institutions consistently appears across multiple scientific fields — forming the backbone of modern AI-driven research. Major ML-enabled studies rarely originate from a single organization; instead, they rely on international partnerships that blend software engineering, domain expertise, and experimental science.
Collaboration patterns vary by region:
- China shows a more concentrated model, with an average of 2.6 organizations per paper.
- The United States demonstrates broader networks, with 4.1 organizations per paper, reflecting its deeply collaborative academic environment.
- India, Saudi Arabia, and the U.S. frequently partner on work in applied sciences, materials research, engineering, and computer vision, forming emerging cross-continental research corridors.
Neural Network Hype vs. Real Impact
Despite the excitement surrounding generative AI, the data shows that scientific research is still powered primarily by mature machine learning methods. Classical ML techniques — including Random Forest, SVMs, and Scikit-learn workflows — account for 47% of all ML use cases.
When combined with established ensemble and clustering methods such as GBM, XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost, these traditional approaches represent a dominant 77% of ML applications in scientific research.
The majority of ML-enabled scientific work focuses on practical, domain-driven objectives — including prediction, classification, image segmentation, biological pattern recognition, protein modeling, and feature extraction — rather than frontier ML innovation.
About Marktechpost
Marktechpost is a global publication covering artificial intelligence, machine learning, and emerging technology research. The platform highlights advances from academic institutions, research labs, and practitioners shaping the future of applied AI. https://www.marktechpost.com/
ContactMedia Dept
[email protected]